What is the climate model?
The state of the climate system and its variability
is determined by the complicated interactions among the physical systems around the Earth's surface;
the atmosphere, the ocean, and the land surface.
This process is so complicated that we cannot work out this by chamber experiments and so on.
It is indeed very important to gather observational data and to analyze them.
However, it is not easy to get enough amount of data since the data which cover the vast scale
in both time and space are needed.
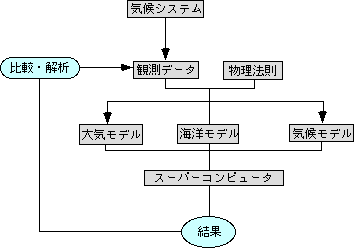
There the research using the climate model
(= the numerical simulation model which imitate the climate system)
which is based upon the physical lows manifests its power.
The climate model is composed of interacting sub-models; atmospheric model,
ocean model, land surface model, and so on.
Supercomputers can simulate the physical quantities such as wind fields,
temperature fields, rainfall amounts, snow amounts, and ocean currents with which
we describe the climate system.
The model has to be improved by comparing the simulated results with observational data.
In this way, we make progress in our understanding of the climate system
by continuous exchange of information between the real and model worlds.
return to Index
return to CCSR homepage
